Calculation Scripts:- Session 8
This is going to be
an interesting session, here we will be learning
different functions and how
to implement them in different scenarios.
Before we do that lets complicate our Hierarchy, We
will be adding one more
Sparse Dimension Years and few more members in our Entity
Dimension.
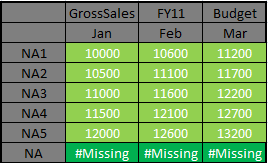
@SUM: This returns the
summation of all the values in a list. We will be taking one more simple
example in which say we need to assign the sum of NA1 to NA5 in the parent
member NA. Lets
lock and send #Missing to below combination.
Now we are sending
some test values for this combination,
I wrote a pretty
simple script
Lets check the result
after executing this script on above data,
Cross Dim operator: A cross Dim operator is used when we have to use two members
from different dimensions, this is one more way to focus our calculations.
We can use this operator when we want to assign/use value at/from a specific
member combination. For Ex: if we need to assign the value of Sales of Jan of
FY11 Actual to Sales of Feb of FY12 budget then one of the way to do
it is:
Sales
(
Sales->Feb->FY12->Budget
= Sales->Jan->FY11->Actuals;
);
And why I have used a
member block here? We have to use cross dimensional operator with in a member
block when we are using cross dim operator at the left hand side of the
equation. Will be implementing the same by an example and will try to
understand average function as well. Lets say we want to calculate the average
gross sales of NA1 to NA5 and need to assign this value to a member called
Average and at NA member from Entity Dimension. Below is the member combination
and we are expecting a Average value at NA->Average,
One of the ways to do
it is by using below script,
After executing this
we will get the following result,
We will be doing the
same using Average function, Average function provides us some additional
functionalities, below is the syntax:
@AVG (SKIPNONE |
SKIPMISSING | SKIPZERO | SKIPBOTH,expList)
we will get the same
result if we use the above script.
If we use SKIPMISSING
option then following will be the result:
Power function: The POWER function returns the value of the specified member
or
expression raised to
power. I will be using Average Account member to demonstrate the functionality
of @Power, Here is the script:
we can even calculate
square root of a number, all we need to do is to pass the
(Expression,.5).Following will be the result of above script:
Boolean Functions: A Boolean function returns a value of TRUE or FALSE, they are
used in
conditional statements. Few of the examples are @ISDESC, @ISMBR,
@ISCHILD, @ISGEN
etc. Lets try to use @ISMBR, If the member is APAC1 then the
Average (Still using the same
member) is 12% of GrossSales, for APAC2 its 15%,
for APAC3 its 18% for rest its 10%. One
of the ways to implements the same is:
Lets find out the
result of this script,
@XRANGE: Its really an
important function, it takes two members as input and returns a
member range,
its useful when we work with two dimensions usually time and period. For ex:
@XRANGE(2010->Nov, 2011->Feb) will return 2010->Nov, 2010->Dec,
2011->Jan, 2011->Feb. Lets take an example to understand it in a better
way. Say we want to calculate the
average Gross Sales of 2010->Jan to
2011->Feb and we want to store the result at Average,
BegBalance of FY10.
lets execute this
script and check the results on below data:
Here we have used
cross dim operator because we were expecting a result at the combination of
Average, BegBalance and FY10.
An important thing to
notice here if we don't mention a member from a dimension to which
member block member belong then member block member is considered from that
dimension,
and operation are restricted to that member only. To make this
statement sensible look at the
last script, here the member block is
of GrossSales Member from Account dimension, in left
hand side we have
mentioned Average but in right hand side we haven't mentioned any
member from
Account dimension, so the right hand side will calculate the sum for GrossSales
member. We will have a detailed discussion on this in later sessions.
ACCUM: The @ACCUM()
function accumulates the values of mbrName within rangeList, up to
the current
member in the dimension of which rangeList is a part. To understand this lets
create
a member call AccumSales in out outline.
This is the data
combination where we are expecting values
Below is a simple
script which will accumulate the values of GrossSales of FY10 to FY14.
After executing this
script we will get the following results:
I know there must be
many thing which can be hard to understand, post your queries (if any) I
will
be more then happy to answer them.
Cheers..!!!
Rahul S.
Rahul S.




















very well explained with examples and colourful tables.
ReplyDelete